Right now the Internet is going through a massive transition, an overhaul of the addresses that will impact every network device connected to it.
What is this overhaul?
How will it change the Internet?
And how will it impact business VoIP telephony?

Big Questions First
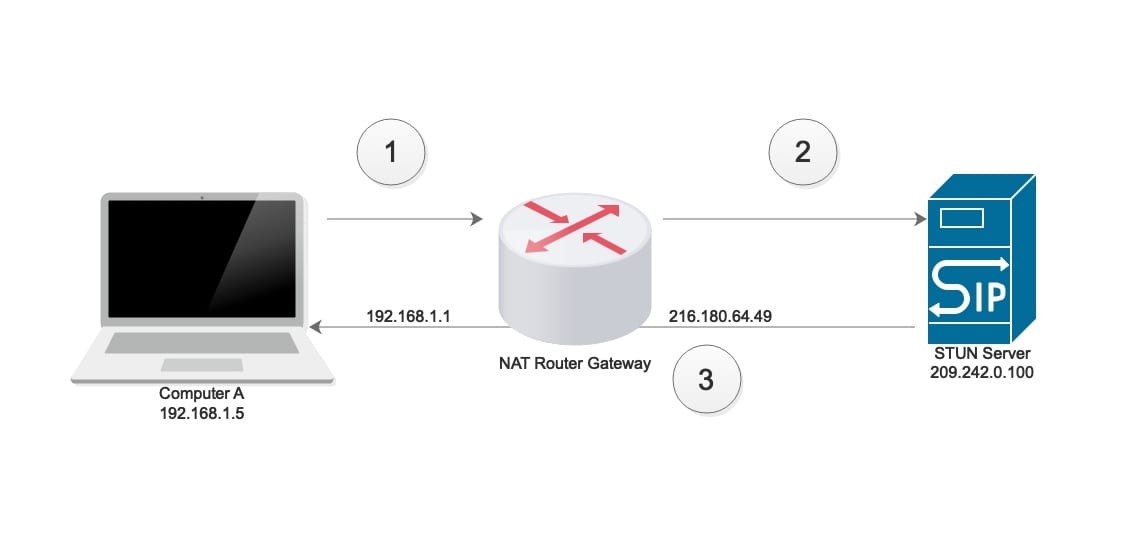
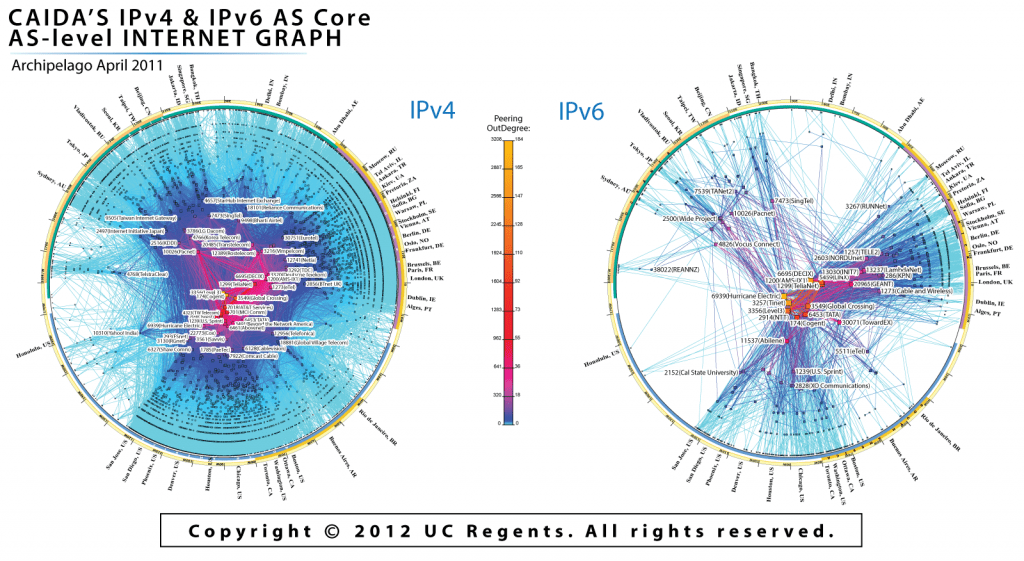
The massive transition we’re talking about here is the change from IPv4 to IPv6, or the change from the old Internet Protocol (IP) system to its newest iteration. Int
Now, the old IP is known as the Internet Protocol Version 4, or the IPv4, and it’s the set of rules that have been in place providing the scaffolding for the Internet since day 1. IPv4 works really well, as most internet communication still occurs using its rules, but we’re now transitioning to the new version of the Internet Protocol, a new set of scaffolding known as the Internet Protocol version 6 or IPv6.ernet Protocol lies at the heart of how the Internet works; it defines the way data packets transfer from one connected device to another over various bundles of equipment, cables and wireless signals. The Internet Protocol outlines the rules for how these data packets are labelled, how they are located, and how they are routed over the web.
So basically we’re in the middle, or more accurately at the beginning, of transition from IPv4 to IPv6.
Read more
 BYOD is a reality, and, by all estimates, it will continue to grow in adoption over the next couple of years, regardless of whether your company officially implements it as a policy or not. Current estimates place BYOD adoption at 60% within the workplace, and projections state BYOD may receive 90% adoption by 2014 alone.
BYOD is a reality, and, by all estimates, it will continue to grow in adoption over the next couple of years, regardless of whether your company officially implements it as a policy or not. Current estimates place BYOD adoption at 60% within the workplace, and projections state BYOD may receive 90% adoption by 2014 alone.